Safety alert over supermarket chickens

The Food Standards Agency (FSA) said it was putting pressure on supermarkets to take action after a year-long study found all the major retailers failed to reach industry targets for reducing rates of campylobacter.
Some 19% of the contaminated chickens were found to contain the highest rate of the bug, which is responsible for an estimated 280,000 cases of food poisoning a year.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdKevin Hargin, the FSA’s head of disease control, said: “This is the FSA’s number one food safety priority, we’re taking it very, very seriously.

“This is the single most common cause of food poisoning, more than Salmonella and Listeria. Salmonella and Listeria might be more serious but this is certainly much more common.
“All of the results are quite disappointing, we didn’t see any significant reductions.”
He added that tackling the spread of the bug was “complex” and supermarkets must make changes throughout the whole production line, from farming to transport and packaging.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe director of consumer body Which? urged supermarkets to commit to “urgent” action to ensure chickens are safe.
Richard Loyd: said “It beggars belief that nearly three-quarters of chickens on sale in supermarkets are still infected with this potentially deadly bug and that no retailers have met the FSA’s target.”
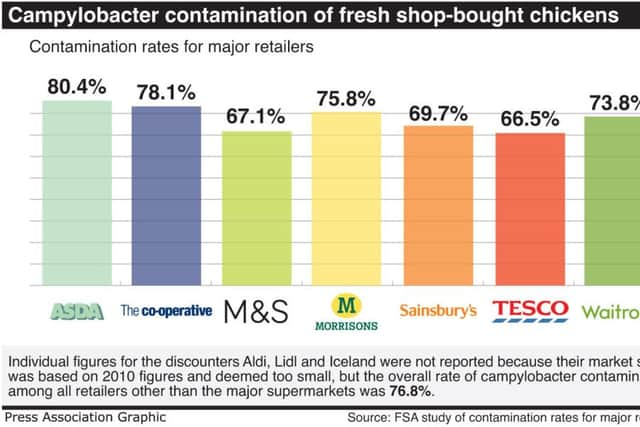
The FSA tests found Asda had the highest rate of contamination in its fresh whole chickens at 80%, followed by Co-op with 78%, Morrisons with 76%, Waitrose with 74%, and Tesco and Marks and Spencer with 67%.
Individual figures for Lidl, Aldi and Iceland are not available because their market share was not considered large enough, based on 2010 retail figures.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdWhile none of the major retailers hit industry targets during the FSA investigation, the food watchdog said new internal case studies by Marks & Spencer, Morrisons, the Co-op and Waitrose based on more recent samples found a fall in contamination levels.
Mr Hargin said: “If some retailers can do it then others should be able to follow suit.
“I think consumers will be concerned and rightly so, we don’t think consumers should be bearing the brunt of the risk.
“We’re continuing to put pressure on the industry to ensure they continue their work with interventions.”
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdConsumers are most likely to pick the bug up through cross-contamination in their kitchen or from eating chicken undercooked.
However, because of a delay in symptoms, they may not realise the illness is caused by their fresh, shop-bought chicken, Mr Hargin added.
In serious cases, contracting the bug from highly contaminated poultry can be fatal.
Dr Georgina Manning, an expert on campylobacter at Nottingham Trent University, said: “Humans become infected when we eat chicken that has been undercooked or we contaminate kitchen surfaces or other foods during the handling of chicken.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide Ad“It is very unpleasant, with symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhoea. In most cases it lasts for just a few days and no treatment other than oral rehydration is necessary. However, in the very young and people who may have a weakened immune system, the symptoms can be more severe and antibiotic treatment or hospitalisation may be needed.
“In order to reduce the levels of campylobacter in chicken the whole of the food chain needs to be considered. Controls on the farm to prevent the bacterium entering the chicken flock are important, along with packaging and labelling to protect and advise the consumer that there is no need to wash the chicken, as this is a major cause of cross contamination in the kitchen.”
A second year of testing will begin this summer to measure the impact of interventions being introduced by the industry to tackle campylobacter.
More than 4,000 samples of fresh whole chickens and packaging from large UK retail outlets and smaller independent stores and butchers were tested.
Q&A ABOUT THE BUG
• What is it?
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdCampylobacter is a bacteria that is the most common cause of food poisoning in the UK. It is thought to be responsible for more than 280,000 cases of food poisoning a year, according to the FSA.
• Where is it found?
It is usually found in raw or undercooked meat, especially poultry, and less often in unpasteurised milk or untreated water. About four in five cases come from contaminated poultry.
• How can infection be prevented?
The FSA recommends:
- covering and chilling raw chicken
- do not wash raw chicken, as this will not kill any bacteria and may spread them around
- wash hands and used utensils with warm, soapy water
- cook chicken thoroughly, until it is steaming hot all the way through, there is no pink meat left and the juices run clear when the meat is cut into
- keep to use-by dates.
• What are the symptoms of campylobacter infection?
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdAs with most food poisoning, the signs are likely to be vomiting, diarrhoea, stomach cramps and pain, loss of appetite, high temperature, aching muscles and chills.
• How long do the symptoms last?
The symptoms usually last for less than a week, and the incubation period between eating contaminated food and feeling ill is two to five days.
• Does food poisoning require medical attention?
Not usually. Food poisoning can normally be treated at home, by drinking plenty of water and resting. Symptoms will be made worse by caffeine, alcohol, fizzy drinks, spicy and fatty foods. If symptoms are severe or do not improve after a few days, the NHS recommends visiting a GP.
The advice is to stay off work or school until at least 48 hours after the last episode of diarrhoea, not to prepare food for other people and to avoid contact with vulnerable people, such as the elderly or very young.
• How can catching an infection be avoided?
To avoid catching the infection from an affected person, regularly wash hands with soap and warm water, and keep surfaces clean.